Artificial satellite of the earth is an object, orbiting the earth, containing radio equipment such as receiver, amplifier, signal processor, transmitter etc, and powered by solar photovoltaic module. First commercial satellite was launched in August 1965. Since then numerous satellites have been launched for communication navigation, defense, broadcasting and other purposes.
Satellite systems may be domestic (used by a single country like Canadian Telecast System or Indian Satellite system-INSAT), regional system used by two or more countries (French-German Symphonic system) and global systems of intercontinental character like INTELSAT, INMARSAT, ASIASAT, INTERSPUTNIK etc. The uses of satellite systems space segment allocation and frequency allocation are coordinated by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) based in Geneva. Specific frequency bands are allocated for use in satellite system:
S-band -2GHz
C-band -4GHz
Ku-band -11GHz
Ka- band -18GHz
In general up-link and down-link frequencies are different to avoid interference.
Satellite stays in the orbit in its position because of balance of centripetal forces on the satellite and the gravitational force of the earth. For this happen the height of the satellite has to be greater than 600 KM from the earth’s surface.
Orbit of Satellite
Orbit is an imaginary path in the space along which the satellite rotates the earth. The basic orbits are elliptical inclined, circular polar and circular equatorial (or as a special case of it-geo-stationary orbit). Circular equatorial orbit situated at the height of about 36,000 KM is called geostationary orbit (or synchronous orbit). Any satellite located at this height will rotate around its axis (23 Hrs. 56 Mins.). In this case the satellite is seen stationary with respect to the earth station. Therefore in practice geostationary orbit satellites are extensively used. Elliptically inclined orbits are used for communication with earth stations located near polar region. Weather forecasting satellites are usually located at lower orbits (Low Earth Orbits-LEO).
Satellite Communication Systems
Satellite contains active elements like receiver, amplifier, signal processor, transmitter antenna etc. Each set of these equipments (transmitter and receiver) is called Transponder. The antenna is common device shared by both receiver and transmitter. The area in the earth surface where the level of signal from the satellite is greater or equal to satisfactory level is called “Foot Print”. As the signal level transmitted by the satellite is very low, the level of received signal is also extremely low. Therefore a special front end amplifier, called Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) is used in the satellite receivers.
The basic types of communication in which satellites are used as active reflectors are:
Direct Satellite Broadcasting Television (DSB-TV)
In DSB-TV system, the TV program generated from the Television studio is transmitted to the satellite. The received signal is then amplified and re-transmitted to the earth by the satellite. The coverage area of the transmitted signal will be wide and individuals can receive this signal and obtain high quality pictures. Examples of DSB-TV are programs of Doordarshan from INSAT and STAR programs from ASIASAT. Terrestrial TV broadcasting stations can receive these signals and retransmit using local transmitters. In this case all the individual users do not need to use expensive satellite receivers.
Fixed Assignment Communication Channel
If heavy communication traffic is known to exist between any two points in the earth, a fixed transponder may be assigned to relay multiplexed signal between these two points. This is called fixed assignment satellite communication. This system does not permit flexibility and has low utilization factor.
Multiple Access System
To increase the satellite utilization factor, most of the satellite systems use Demand Assigned Multiple Access (DAMA) system. In this system the earth station A desirous to establish communication with another earth station B send request signal to satellite. The satellite assigns the station A any of the free channel, presently unoccupied, to establish link between A and B. The assignment could be in frequency slot (FDM) or in time slot (TDM). If the assignment is in frequency slot, the system is called Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA). In case of time slot assignment, the system is called Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA).
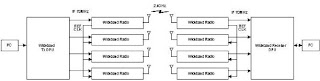
A good example of FDMA is SPADE System (Single Channel Per Carrier PCM Multiple Access Demand Assignment Equipment). In this system a common pool of about 800 channels (carriers) are available to all ground stations having common signaling channel. If station A wishes to establish link with station B, the former selects a free channel randomly and though the signaling link send the information on the selected channel. When the station B confirms it, the link is established. Because of various constraints in using FDM, present satellite systems use only TDMA.
Satellite systems may be domestic (used by a single country like Canadian Telecast System or Indian Satellite system-INSAT), regional system used by two or more countries (French-German Symphonic system) and global systems of intercontinental character like INTELSAT, INMARSAT, ASIASAT, INTERSPUTNIK etc. The uses of satellite systems space segment allocation and frequency allocation are coordinated by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) based in Geneva. Specific frequency bands are allocated for use in satellite system:
S-band -2GHz
C-band -4GHz
Ku-band -11GHz
Ka- band -18GHz
In general up-link and down-link frequencies are different to avoid interference.
Satellite stays in the orbit in its position because of balance of centripetal forces on the satellite and the gravitational force of the earth. For this happen the height of the satellite has to be greater than 600 KM from the earth’s surface.
Orbit of Satellite
Orbit is an imaginary path in the space along which the satellite rotates the earth. The basic orbits are elliptical inclined, circular polar and circular equatorial (or as a special case of it-geo-stationary orbit). Circular equatorial orbit situated at the height of about 36,000 KM is called geostationary orbit (or synchronous orbit). Any satellite located at this height will rotate around its axis (23 Hrs. 56 Mins.). In this case the satellite is seen stationary with respect to the earth station. Therefore in practice geostationary orbit satellites are extensively used. Elliptically inclined orbits are used for communication with earth stations located near polar region. Weather forecasting satellites are usually located at lower orbits (Low Earth Orbits-LEO).
Satellite Communication Systems
Satellite contains active elements like receiver, amplifier, signal processor, transmitter antenna etc. Each set of these equipments (transmitter and receiver) is called Transponder. The antenna is common device shared by both receiver and transmitter. The area in the earth surface where the level of signal from the satellite is greater or equal to satisfactory level is called “Foot Print”. As the signal level transmitted by the satellite is very low, the level of received signal is also extremely low. Therefore a special front end amplifier, called Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) is used in the satellite receivers.
The basic types of communication in which satellites are used as active reflectors are:
Direct Satellite Broadcasting Television (DSB-TV)
In DSB-TV system, the TV program generated from the Television studio is transmitted to the satellite. The received signal is then amplified and re-transmitted to the earth by the satellite. The coverage area of the transmitted signal will be wide and individuals can receive this signal and obtain high quality pictures. Examples of DSB-TV are programs of Doordarshan from INSAT and STAR programs from ASIASAT. Terrestrial TV broadcasting stations can receive these signals and retransmit using local transmitters. In this case all the individual users do not need to use expensive satellite receivers.
Fixed Assignment Communication Channel
If heavy communication traffic is known to exist between any two points in the earth, a fixed transponder may be assigned to relay multiplexed signal between these two points. This is called fixed assignment satellite communication. This system does not permit flexibility and has low utilization factor.
Multiple Access System
To increase the satellite utilization factor, most of the satellite systems use Demand Assigned Multiple Access (DAMA) system. In this system the earth station A desirous to establish communication with another earth station B send request signal to satellite. The satellite assigns the station A any of the free channel, presently unoccupied, to establish link between A and B. The assignment could be in frequency slot (FDM) or in time slot (TDM). If the assignment is in frequency slot, the system is called Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA). In case of time slot assignment, the system is called Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA).
A good example of FDMA is SPADE System (Single Channel Per Carrier PCM Multiple Access Demand Assignment Equipment). In this system a common pool of about 800 channels (carriers) are available to all ground stations having common signaling channel. If station A wishes to establish link with station B, the former selects a free channel randomly and though the signaling link send the information on the selected channel. When the station B confirms it, the link is established. Because of various constraints in using FDM, present satellite systems use only TDMA.