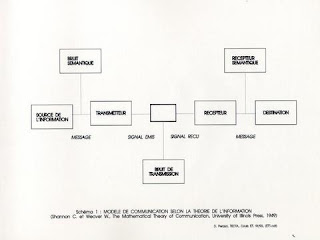
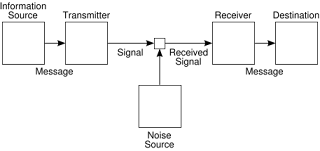
Communication is the process of establishing connection or link between two points for information exchange. OR The purpose of communication system is to transmit information bearing signals from a source located at one point to a user destination located at another point some distance away.
Communication is simply the process of conveying message at a distance or communication is the basic process of exchanging information. The electronic equipments which are used for communication purpose, are called communication equipments. Different communication equipments when assembled together form a communication system.
Typical examples of communication systems are line telephony and line telegraphy, radio telephony and radio telegraphy, radio broadcasting, point-to-point communication and mobile communication, computer communication, radar communication, television broadcasting, radio aids to navigation, radio aids to aircraft landing etc.
The earliest communication system namely line-telegraphy originated in eighteen forties (1840s). In addition to this, line telephony came a few decades later whereas radio-communication could become possible in the beginning of twent ieth century on invention of triode valve. Radio communication was further greatly improved during World War II. It becomes more widely used through the invention of transistor, integrated circuits (ICS) and other Semiconductor devices in the subsequent years. Also in recent years, communication has become more widespread with the use or satellites and fiber optics. Today, there has been an increasing emphasis on the use of computer in communication.
ieth century on invention of triode valve. Radio communication was further greatly improved during World War II. It becomes more widely used through the invention of transistor, integrated circuits (ICS) and other Semiconductor devices in the subsequent years. Also in recent years, communication has become more widespread with the use or satellites and fiber optics. Today, there has been an increasing emphasis on the use of computer in communication.
Elements of Communication System (communication Process)
The essential components of communication system are information source, input transducer, transmitter, communication channel, receiver and destination.
(1) Information source : We know that a communication system serves to communicate a message signal or information. The information or message signal is originated from information source. Source of information generates message signal examples of which are human voice, telephone pictures, teletype data, atmospheric temperature and pressure in the above example.
In short, we can say that the function of information source is to produce required message signal which has to be transmitted.
(2) Input Transducer : A transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. The message from the information source may or may not electrical in nature. In a case when the message signal produced by information source is not electrical in nature, an input transducer is used to convert it into a time varying electrical signal. For example, in case of radio-broadcasting, a microphone converts the information or message which is in the form of sound waves into corresponding electrical signal.
(3) Transmitter : The function of transmitter is to process the electrical signal from different aspects. The signal received from the information source after converting it into electrical signal is not suitable for transmission over the channel. The message signal requires same processing like filtering and modulation etc, so that it is suitable for the transmission over the channel. Inside the transmitter, signal processing such as restriction of range of audio frequencies, amplification and modulation are achieved. All these processing of the message signal are done just to ease the transmission of the signal through the channel.
(4) Channel : The physical connection between transmitter output and receiver input is provided by the channel. There are mainly two types of channels.
a. Point to point channel
b. Broad cast channel
a. Point to point channel : The point to point channels are wirelines, microwave links, optical fibers. The wirelines are operated by guided electromagnetic waves used in local telephone transmission. In microwave links, the transmitted signal is radiated as an electromagnetic wave in free space and or used in long distance communication. An optical fiber is lowless well controlled, guided optical medium used in optical fiber communication system.
b. Broadcast channel : Broadcast channels provides a capability where several receiving stations can be reached simultaneously from a single transmitter.An examples of Broadcast channels is a satellite in geostationary orbit, which covers one third of earth’s surface.
Noise : Noise is an unwanted signal which tend to interface with the required with the required signal. Noise signal is always random in character. Noise may interfere with signal at any point in a communication system. However, the noise has its greatest effect on the signal in the channel.
(5) Receiver : The signals received at the output of the channel consists of noise along when information carrying signals must be separated from carrier wave and noise introduce by the channel. The receiver performs the estimation of original message signal. This operation of receiver is called demodulation.
(6) Destination : Destination is the final stage which is used to convert an electrical message signal into its original form. For example in radio broadcasting, the destination is a loudspeaker which works as a transducer i.e. it converts the electrical signal form of original sound signal.
Communication System, can be classified as
1. Analog Communication and
2. Digital Communication
1. Analog Communication : Analog Communication is that type of communication in which the message or information signal i.e. transmitted is analog in nature. This means that in analog communication modulating signal (i.e. baseband signals) is analog signal. This analog message signal may be obtained form sources such as speech, video shooting etc.
In analog communication, the analog message signal modulates some high carrier frequency inside the transmitter to produce modulating signal. This modulated signal is then transmitted with the help of a transmitting antenna to travel through the transmission channel. At the receiver, this modulated signal is received and processed to recover the original message signal. Presently all the AM, FM radio transmission and TV transmission are examples of analog communication system.
The block diagram of analog communication system consists of
a. Input transducer
b. Transmitter
c. Channel
d. Distortion and Noise
e. Receiver
f. Output Transducer
All of this components has been described in previous elements of communication system.
Typical examples of communication systems are line telephony and line telegraphy, radio telephony and radio telegraphy, radio broadcasting, point-to-point communication and mobile communication, computer communication, radar communication, television broadcasting, radio aids to navigation, radio aids to aircraft landing etc.
The earliest communication system namely line-telegraphy originated in eighteen forties (1840s). In addition to this, line telephony came a few decades later whereas radio-communication could become possible in the beginning of twent
 ieth century on invention of triode valve. Radio communication was further greatly improved during World War II. It becomes more widely used through the invention of transistor, integrated circuits (ICS) and other Semiconductor devices in the subsequent years. Also in recent years, communication has become more widespread with the use or satellites and fiber optics. Today, there has been an increasing emphasis on the use of computer in communication.
ieth century on invention of triode valve. Radio communication was further greatly improved during World War II. It becomes more widely used through the invention of transistor, integrated circuits (ICS) and other Semiconductor devices in the subsequent years. Also in recent years, communication has become more widespread with the use or satellites and fiber optics. Today, there has been an increasing emphasis on the use of computer in communication.Elements of Communication System (communication Process)
The essential components of communication system are information source, input transducer, transmitter, communication channel, receiver and destination.
(1) Information source : We know that a communication system serves to communicate a message signal or information. The information or message signal is originated from information source. Source of information generates message signal examples of which are human voice, telephone pictures, teletype data, atmospheric temperature and pressure in the above example.
In short, we can say that the function of information source is to produce required message signal which has to be transmitted.
(2) Input Transducer : A transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. The message from the information source may or may not electrical in nature. In a case when the message signal produced by information source is not electrical in nature, an input transducer is used to convert it into a time varying electrical signal. For example, in case of radio-broadcasting, a microphone converts the information or message which is in the form of sound waves into corresponding electrical signal.
(3) Transmitter : The function of transmitter is to process the electrical signal from different aspects. The signal received from the information source after converting it into electrical signal is not suitable for transmission over the channel. The message signal requires same processing like filtering and modulation etc, so that it is suitable for the transmission over the channel. Inside the transmitter, signal processing such as restriction of range of audio frequencies, amplification and modulation are achieved. All these processing of the message signal are done just to ease the transmission of the signal through the channel.
(4) Channel : The physical connection between transmitter output and receiver input is provided by the channel. There are mainly two types of channels.
a. Point to point channel
b. Broad cast channel
a. Point to point channel : The point to point channels are wirelines, microwave links, optical fibers. The wirelines are operated by guided electromagnetic waves used in local telephone transmission. In microwave links, the transmitted signal is radiated as an electromagnetic wave in free space and or used in long distance communication. An optical fiber is lowless well controlled, guided optical medium used in optical fiber communication system.
b. Broadcast channel : Broadcast channels provides a capability where several receiving stations can be reached simultaneously from a single transmitter.An examples of Broadcast channels is a satellite in geostationary orbit, which covers one third of earth’s surface.
Noise : Noise is an unwanted signal which tend to interface with the required with the required signal. Noise signal is always random in character. Noise may interfere with signal at any point in a communication system. However, the noise has its greatest effect on the signal in the channel.
(5) Receiver : The signals received at the output of the channel consists of noise along when information carrying signals must be separated from carrier wave and noise introduce by the channel. The receiver performs the estimation of original message signal. This operation of receiver is called demodulation.
(6) Destination : Destination is the final stage which is used to convert an electrical message signal into its original form. For example in radio broadcasting, the destination is a loudspeaker which works as a transducer i.e. it converts the electrical signal form of original sound signal.
Communication System, can be classified as
1. Analog Communication and
2. Digital Communication
1. Analog Communication : Analog Communication is that type of communication in which the message or information signal i.e. transmitted is analog in nature. This means that in analog communication modulating signal (i.e. baseband signals) is analog signal. This analog message signal may be obtained form sources such as speech, video shooting etc.
In analog communication, the analog message signal modulates some high carrier frequency inside the transmitter to produce modulating signal. This modulated signal is then transmitted with the help of a transmitting antenna to travel through the transmission channel. At the receiver, this modulated signal is received and processed to recover the original message signal. Presently all the AM, FM radio transmission and TV transmission are examples of analog communication system.
The block diagram of analog communication system consists of
a. Input transducer
b. Transmitter
c. Channel
d. Distortion and Noise
e. Receiver
f. Output Transducer
All of this components has been described in previous elements of communication system.