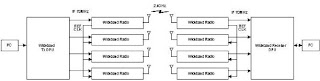
Multiplexing is a technique whereby a number of independent signals can be combined into a composite signal suitable for transmission over a common channel voice frequencies transmitted over telephone systems, for example, range from 300 to 3100 HZ. To transmit a number of these signals over the same channel, the signals must be kept apart so that they do not interfere with eachother, and thus they can be serperated at the receiving end. Thies is accomplished by separating these signals either in frequency or in time. The technique fo separating the signals in frequency is referred to as frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), whereas, the technique of separating the signals in time is referred as time-division multiplexing (TDM).
The Components of a FDM System are
Message signal
Transmitter consists of product modulators and oscillators
Side band Filters
Band pass Filters
Receiver or detector
Low pass filter
The incoming message signals are assumed to be of the low pass type, but their spectra donot necessarily non zero values all the way down to zero frequency. A low pass filter, when is designed to remove high-frequency component. These low pass filters may be omitted only if the input signals are sufficiency band limited initially. The filtered signals are applied to modulators that shift the frequency ranges of the signals so as to occupy mutually exclusively frequency intervals. The necessary carrier frequencies needed to perform these frequency translation are obtained from carrier supply. The most widely used method of modulation in frequency-division multiplexing is single side band modulation, which in the case of voice signals, requires a bandwidth that is approximately equal to that of the original voice signal. In practice, each voice input is usually assigned a bandwidth of 4KHZ. The band to restrict the band of each modulated wave to its prescribed range. The resulting band pass filters outputs are next combined in parallel to form the input to the common channel. At the receiving terminal, a bank of band-pass filters with their inputs connected in parallel is used to separate the message signals on a frequency occupancy basis. Finally the original message signals are recovered by individual demodulators.
Frequency in Telephony
FDM is extensively used in telephone to transmit number of telephone channels simultaneously over a channel of cable or microwave link. Basic telephone channel is bandlimited to 300-3400HZ (bandwidth 3100HZ). A frequency slot of 4 KHZ is assigned to each telephone channel so that there is a guard band of 900HZ for each channel. The first three channels are multiplexed at 12,16 and 20 KHZ to form a pre-group of 3 telephone channels. The multiplexing (frequency shifting) is SSB-USB. The total bandwidth of the pre-group consisting of three telephone channels is 12KHZ.
Four set of pre-group produce 12 channel group carrier frequencies 60, 72, 84 and 96KHZ is assigned to each pre-group. The bandwidth of the 12 group channel is 48KHZ.
Five sets of 12 channel group produce 60 channel super group. The frequencies assigned are 312, 360, 408, 456, 504 and 552 KHZ. The bandwidth of super group is 240KHZ.
Ten sets of super group produces Master group of 600 voice channels with the bandwidth of 2500KHZ. Finally, six sets of master group produce super master group with a bandwidth of 17MHZ.
Television signal can also transmitted over the voice channel. As the composite video signal (video plus Fm audio) bandwidth is about 6MHZ a super master group can be used for simultaneous transmission of two television channels and about 1200 voice channels.
The Components of a FDM System are
Message signal
Transmitter consists of product modulators and oscillators
Side band Filters
Band pass Filters
Receiver or detector
Low pass filter
The incoming message signals are assumed to be of the low pass type, but their spectra donot necessarily non zero values all the way down to zero frequency. A low pass filter, when is designed to remove high-frequency component. These low pass filters may be omitted only if the input signals are sufficiency band limited initially. The filtered signals are applied to modulators that shift the frequency ranges of the signals so as to occupy mutually exclusively frequency intervals. The necessary carrier frequencies needed to perform these frequency translation are obtained from carrier supply. The most widely used method of modulation in frequency-division multiplexing is single side band modulation, which in the case of voice signals, requires a bandwidth that is approximately equal to that of the original voice signal. In practice, each voice input is usually assigned a bandwidth of 4KHZ. The band to restrict the band of each modulated wave to its prescribed range. The resulting band pass filters outputs are next combined in parallel to form the input to the common channel. At the receiving terminal, a bank of band-pass filters with their inputs connected in parallel is used to separate the message signals on a frequency occupancy basis. Finally the original message signals are recovered by individual demodulators.
Frequency in Telephony
FDM is extensively used in telephone to transmit number of telephone channels simultaneously over a channel of cable or microwave link. Basic telephone channel is bandlimited to 300-3400HZ (bandwidth 3100HZ). A frequency slot of 4 KHZ is assigned to each telephone channel so that there is a guard band of 900HZ for each channel. The first three channels are multiplexed at 12,16 and 20 KHZ to form a pre-group of 3 telephone channels. The multiplexing (frequency shifting) is SSB-USB. The total bandwidth of the pre-group consisting of three telephone channels is 12KHZ.
Four set of pre-group produce 12 channel group carrier frequencies 60, 72, 84 and 96KHZ is assigned to each pre-group. The bandwidth of the 12 group channel is 48KHZ.
Five sets of 12 channel group produce 60 channel super group. The frequencies assigned are 312, 360, 408, 456, 504 and 552 KHZ. The bandwidth of super group is 240KHZ.
Ten sets of super group produces Master group of 600 voice channels with the bandwidth of 2500KHZ. Finally, six sets of master group produce super master group with a bandwidth of 17MHZ.
Television signal can also transmitted over the voice channel. As the composite video signal (video plus Fm audio) bandwidth is about 6MHZ a super master group can be used for simultaneous transmission of two television channels and about 1200 voice channels.

No comments:
Post a Comment